Division
Division is splitting into equal parts or groups.
It is the result of "fair sharing".
Example: there are 12 chocolates, and 3 friends want to share them, how do they divide the chocolates?
12 Chocolates
12 Chocolates Divided by 3
Answer: 12 divided by 3 is 4. They get 4 each.
Symbols
We use the ÷ symbol, or sometimes the / symbol to mean divide:
| 12 ÷ 3 = 4 12 / 3 = 4 |
Let's use both symbols here so we get used to them.
More Examples
Here are some more examples:
Opposite of Multiplying
Division is the opposite of multiplying. When we know a multiplication fact we can find a division fact:
Example: 3 × 5 = 15, so 15 / 5 = 3.
Also 15 / 3 = 5.
Why? Well, think of the numbers in rows and columns like in this illustration:
| Multiplication... | ...Division | |
|---|---|---|
| 3 groups of 5 make 15... | ...so 15 divided by 3 is 5 | |
|
and also: |
||
| 5 groups of 3 make 15... | ...so 15 divided by 5 is 3. | |
So there are four related facts:
- 3 × 5 = 15
- 5 × 3 = 15
- 15 / 3 = 5
- 15 / 5 = 3
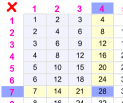
Knowing your Multiplication Tables can help you with division!
Example: What is 28 ÷ 7 ?
Searching around the multiplication table we find that 28 is 4 × 7, so 28 divided by 7 must be 4.
Answer: 28 ÷ 7 = 4
Names
There are special names for each number in a division:
dividend ÷ divisor = quotient
Example: in 12 ÷ 3 = 4:
- 12 is the dividend
- 3 is the divisor
- 4 is the quotient
But Sometimes It Does Not Work Perfectly!
Sometimes we cannot divide things up exactly ... there may be something left over.
Example: There are 7 bones to share with 2 pups.
But 7 cannot be divided exactly into 2 groups,
so each pup gets 3 bones,
but there will be 1 left over:
We call that the Remainder.
Read more about this at Division and Remainders
Exercises
Try these division worksheets.