Introduction to Algebra
Algebra is great fun - we get to solve puzzles!
A Puzzle
What is the missing number?
OK, the answer is 6, right? Because 6 − 2 = 4. Easy stuff.
Well, in Algebra we don't use blank boxes, we use a letter (usually an x or y, but any letter is fine). So we write:
It is really that simple. The letter (in this case an x) just means "we don't know this yet", and is often called the unknown or the variable.
And when we solve it we write:
Why Use a Letter?
Because:
- it is easier to write "x" than drawing empty boxes (and easier to say "x" than "the empty box")
- if there are several empty boxes (several "unknowns") we can use a different letter for each one
So x is simply better than having an empty box. We aren't trying to make words with it!
And it doesn't have to be x, it could be y or w ... or any letter or symbol we like.
How to Solve
Algebra is just like a puzzle where we start with something like "x − 2 = 4" and we want to end up with something like "x = 6".
But instead of saying "obviously x=6", use this neat step-by-step approach:
- Work out what to remove to get "x = ..."
- Remove it by doing the opposite (adding is the opposite of subtracting)
- Do that to both sides
Here is an example:
to remove
the "−2"
To remove it, do
the opposite, in
this case add 2
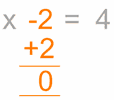
Do it to
both sides
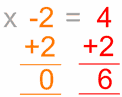
Which is ...
Solved!
Why did we add 2 to both sides?
To "keep the balance"...
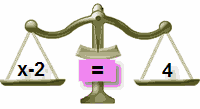 |
| In Balance |
| Add 2 to Left Side |
 |
| Out of Balance! |
| Add 2 to Right Side Also |
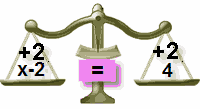 |
| In Balance Again |
To keep the balance, what we do to one side of the "="
we must also do to the other side!
Try this yourself at the Algebra Balance Animation.
Another Puzzle
Example: Solve x + 5 = 12
We want x by itself, but the +5 is in the way. Let's remove it by doing the opposite: let's subtract 5 from both sides.
(Check: Does 7 + 5 = 12?, Yes!)
Have a Try Yourself
Now practice on this Simple Algebra Worksheet and then check your answers. Try to use the steps we have shown you here, rather than just guessing!
Also try the questions below, then move on to Introduction to Algebra - Multiplication