Symbols in Geometry
Common Symbols Used in Geometry
Symbols save time and space when writing. Here are the most common geometrical symbols (also see Symbols in Algebra):
| Symbol | Meaning | Example | In Words |
|---|---|---|---|
| △ | Triangle | △ABC has 3 equal sides | Triangle ABC has three equal sides |
| ∠ | Angle | ∠ABC is 45° | The angle formed by ABC is 45 degrees. |
| ⊥ | Perpendicular | AB⊥CD | The line AB is perpendicular to line CD |
| ∥ | Parallel | EF∥GH | The line EF is parallel to line GH |
| ° | Degrees | 360° | 360 degrees (a full rotation!) |
| ∟ | Right Angle (90°) | ∟ is 90° | A right angle is 90 degrees |
| |
Line Segment "AB" | The line segment between A and B | |
| |
Ray "AB" | The line that starts at A, goes through B and continues on | |
| |
Line "AB" | |
The infinite line that includes A and B |
| ⌒ | Arc | ⌒AB | The curved path between point A and B |
| ≅ | Congruent (same shape and size) | △ABC ≅ △DEF |
Triangle ABC is congruent to triangle DEF |
| ∼ | Similar (same shape, different size) | △DEF∼△MNO | Triangle DEF is similar to triangle MNO |
| ∴ | Therefore | a=b |
a equals b, therefore b equals a |
Example: In △ABC, ∠BAC is ∟
Is really saying: "In triangle ABC, the angle BAC is a right angle"
Naming Angles
For angles the central letter is where the angle is.
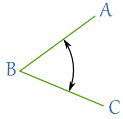
Example: ∠ABC is 45°
The point "B" is where the angle is.
3262, 3263, 3264, 3265, 3266, 3267, 3268, 3269, 5154, 5155